Bringing a new invention from a mere idea to a marketable product is a challenging yet rewarding journey. It involves a series of well-defined steps, each crucial for the successful commercialization of your invention. This article will guide you through these essential stages, providing insights and tips to help you navigate the process effectively.
1. Idea Conception and Validation
The first step in the journey is to thoroughly validate your idea. This involves brainstorming, researching existing solutions, and evaluating the uniqueness and feasibility of your invention. Ask yourself key questions: Does it solve a real problem? Is there a market need for it? Conducting preliminary market research and seeking feedback from potential users can provide valuable insights.
2. Conducting Market Research
Market research is critical to understanding your target audience, competitors, and market trends. Identify your potential customers and gather information on their needs, preferences, and purchasing behavior. Analyze your competitors to understand their strengths and weaknesses. This data will help you refine your invention and develop a compelling value proposition.
3. Prototyping
Creating a prototype is a crucial step to bring your idea to life. A prototype helps you test the functionality, design, and usability of your invention. It doesn’t have to be perfect initially; even a basic version can provide valuable feedback. Iterate on your prototype based on user testing and feedback to improve its design and functionality.
4. Securing Intellectual Property
Protecting your intellectual property (IP) is essential to safeguard your invention from being copied. Depending on the nature of your invention, you may need to file for a patent, trademark, or copyright. Consult with a patent attorney to understand the best strategy for protecting your IP. A strong IP portfolio can also enhance your credibility and attract investors.
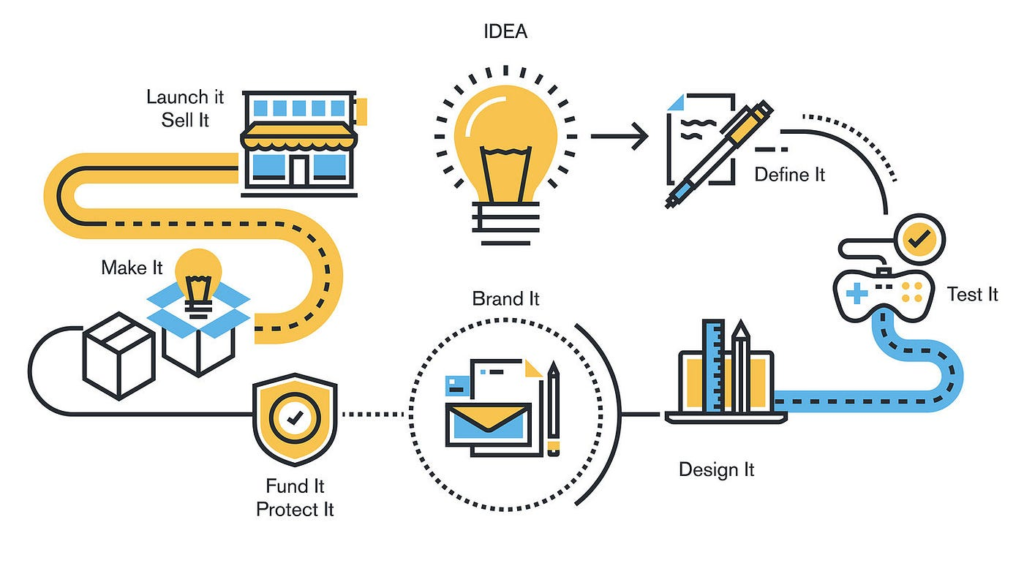
5. Developing a Business Plan
A well-crafted business plan outlines your strategy for bringing the invention to market. It should include an executive summary, market analysis, marketing and sales strategies, operational plan, and financial projections. A comprehensive business plan not only guides your commercialization efforts but also serves as a vital document for securing funding.
6. Funding Your Invention
Securing funding is often one of the biggest challenges inventors face. Explore various funding options such as personal savings, loans, grants, angel investors, venture capital, and crowdfunding. Each option has its pros and cons, so choose the one that best fits your needs and circumstances. A strong business plan and prototype can significantly enhance your chances of attracting investors.
7. Product Development and Manufacturing
Once you have the necessary funding, move forward with the development and manufacturing of your invention. This stage involves finalizing the design, selecting materials, and finding reliable manufacturers. Quality control is critical to ensure that the final product meets the desired standards and performs as intended.
8. Creating a Go-to-Market Strategy
Your go-to-market strategy outlines how you will launch your product and reach your target audience. This includes defining your marketing and sales channels, pricing strategy, and promotional activities. Consider both online and offline channels to maximize your reach. Pre-launch activities such as building a website, creating social media profiles, and generating buzz can help create anticipation for your product.
9. Marketing and Sales
Effective marketing and sales strategies are essential for driving awareness and generating sales. Utilize digital marketing techniques such as SEO, content marketing, social media advertising, and email campaigns. Attend trade shows, exhibitions, and networking events to showcase your invention and connect with potential buyers and partners. Establishing a strong online and offline presence will help you reach a broader audience.
10. Distribution and Customer Service
Finally, establish a robust distribution network to ensure your product reaches your customers efficiently. This may involve partnering with retailers, setting up an e-commerce platform, or using third-party logistics providers. Providing excellent customer service is crucial for building trust and loyalty. Address customer inquiries and feedback promptly to enhance their experience and satisfaction.
Conclusion
The journey from idea to market is a multifaceted process that requires careful planning, perseverance, and adaptability. By following these steps, you can navigate the complexities of commercialization and increase the chances of success for your invention. Remember, every successful product started as a simple idea, and with dedication and strategic planning, your invention can make a significant impact in the market.

